People who follow a vegetarian diet don’t consume meat or fish but a limited amount of people still consumes dietary products and egg.
A few reports confirm that a vegetarian diet can help you prevent some chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Some diets depend on proceed food, too much of calories and sugar. That can affect your overall health. In the diet list, they didn’t add fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
That’s why we created this blog here you can find vegetarian benefits, risks, and tips.
We also added a list of vegetarian foods which contains all the nutrients, proteins, and minerals. The best part is all age group people can follow this diet chat.
What Kind of Food Vegetarians Consuming?
People who follow a vegetarian diet prefer to consume vegetables, fruits, and dietary foods.
Another important thing, while making a diet plan they should choose foods that can full fill all the proteins, nutrients, and minerals of your body.
Types of Vegetarian Diet?
There are several types of vegetarian diets, each with its own specific guidelines regarding which foods are included or excluded. Here are the most common types:
Vegan
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and honey. It is purely plant-based.
Lacto-vegetarian
This diet includes dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, in addition to plant-based foods. Meat, fish, eggs, and poultry are excluded.
Lacto-ovo-vegetarian
This type of vegetarian diet includes both dairy products and eggs, along with plant-based foods. Meat and fish are not consumed.
Ovo-vegetarian
An ovo-vegetarian diet includes eggs but excludes all other animal products, including meat, fish, poultry, and dairy.
Pescatarian
Although not strictly vegetarian, pescatarians exclude meat but include fish and seafood in their diet, along with plant-based foods.
Benefits of the Vegetarian Diet
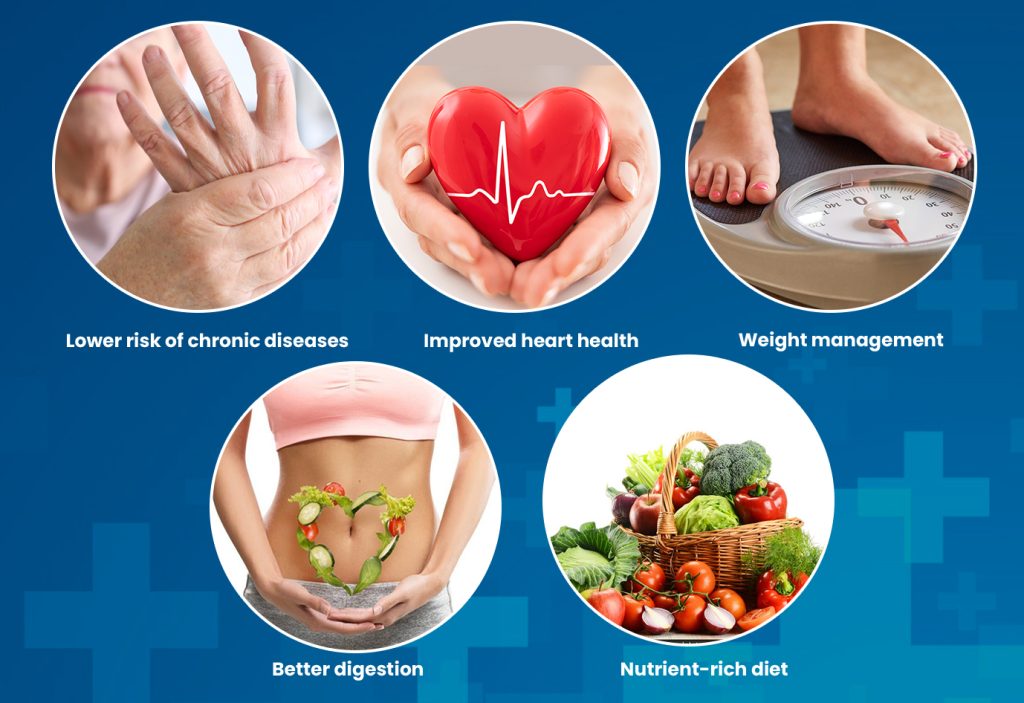
Lower risk of chronic diseases
A well-balanced diet can reduce the risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer (such as colon, breast, and prostate cancer), and obesity. This is mainly due to the higher intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, which are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and various nutrients.
Improved heart health
Plant-based diets don't contain saturated fat and cholesterol, which helps you maintain cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. These are rich in fiber, potassium, and antioxidants, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Weight management
Vegetarian diets, particularly those that are high in whole, unprocessed plant foods, can be effective for weight management and weight loss. Plant-based foods tend to be lower in calories and higher in fiber, which helps increase feelings of fullness and satiety, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
Better digestion
In the vegetarian diet chart fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes are included. It helps to improve your digestion system and prevent constipation. The fiber content aids in maintaining regular bowel movements and promotes a healthy gut microbiome.
Nutrient-rich diet
A vegetarian diet can full fill all the necessary nutrients and proteins the body needs for optimal health. Plant-based foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients, vitamin C, vitamin E, folate, magnesium, potassium, and antioxidants.
However, it's important to pay attention to specific nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids which may require special attention in a vegetarian diet.
Environmental sustainability
Plant-based diets have a lower carbon footprint and require fewer resources, such as land, water, and energy, compared to diets heavy in animal products. By choosing a vegetarian diet, individuals can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Diet
Plan your meals
Take some time to plan your meals in advance. This will help ensure that you have a variety of nutritious foods and ingredients on hand. Include a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds to meet your nutritional needs.
Include a variety of plant-based proteins
To replace the protein usually obtained from meat, include a variety of plant-based protein sources in your diet, such as beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, seitan, quinoa, and edamame. This will help ensure you're getting all the essential amino acids.
Incorporate whole grains
Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, oats, and barley instead of refined grains. Whole grains provide more fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Get enough iron
Plant-based sources of iron include spinach, kale, lentils, beans, fortified cereals, tofu, and pumpkin seeds. To enhance iron absorption, pair iron-rich foods with a source of vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, or bell peppers.
Include healthy fats
Incorporate sources of healthy fats into your diet, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are important for nutrient absorption and provide essential fatty acids.
Pay attention to vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based products, so it's important for vegetarians to ensure adequate intake. Include fortified plant-based milk, cereals, or take a B12 supplement as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Calcium sources
Include calcium-rich foods in your diet to support bone health. Good plant-based sources of calcium include leafy greens (like kale and collard greens), broccoli, fortified plant-based milk, tofu, and almonds.
Experiment with new recipes and flavors
Explore vegetarian recipes from different cuisines to keep your meals exciting and diverse. There are countless delicious vegetarian recipes available that showcase the flavors of various cultures.
For more health-related information click
here.
Conclusion
Here in this blog, we discussed various things about a vegetarian diet's risk factors and benifits. If you follow a vegetarian diet then read carefully to in detail in detail information.

